I’m excited to be presenting, “The 1909 Murder of Ignatii Dvernitskii: A microhistorical approach,” as part of a panel on microhistory approaches to Russian and Soviet history at the annual convention of the Canadian Association of Slavists, part of the larger Congress of the Humanities and Social Sciences that will take place at Ryerson University later this month. This paper will expand on the paper I presented at the Dostoevsky conference in the Fall, and follow a few of the threads that, I think, show the significance of the murder for understanding late-Tsarist Siberia: education, the press, conservatism, anti-Semitism, Dostoevsky, and student activism.
There are a few aspects of the panel that are particularly exciting for me. Nigel Raab is chairing the panel, and aside from his work on Russia, he is also the author of the recent, Who Is the Historian?, an excellent book on historical methods that I assigned in HIST 3000, “The Historian’s Craft,” here at TRU in Fall 2016. One aspect of the book I particularly like is its emphasis on the research and writing of history as a collaborative process. On that note, I want to give a shout-out to my excellent research assistants (three in 2016-2017, and four in 2015-2016) who have helped me with the 44 Lenina project so far (I won’t mention their names without explicit permission, so perhaps in another post). Their work has been invaluable, particularly related to issues of memory and memorials, the murder of Dvernitskii, and the topics of religion and punishment in the late Tsarist era. One of these assistants even accompanied me for part of my research trip to Tomsk, last summer. While on the collaborative methodology note, it’s also worth emphasizing that none of this would be possible without the work of the archivists, librarians, and museum staff of the Tomsk research venues, as well as the inter-library loan librarians here at TRU. Funding for the entire project has come directly from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC), a research grant I would not have won without the help of TRU’s Office of Research and Graduate Studies. And, of course, I’ve received tremendous support from friends, colleagues, and, most importantly, my family. I’m certainly far from alone on this project! Thank you, everyone!
I’m also excited to be presenting with two amazing panelists. Alison Smith is the author of two great books on Imperial Russia, and was the “internal external” reader on my doctoral thesis at the University of Toronto. My approach to the murder of Ignatii is partially inspired by her incredible blog posts on “Russian History Blog,” including the very engaging series on the death of the cheese master. To me, her posts demonstrate the value of microhistorical approaches to Russia’s history. The other panelist, Alan Barenberg, is a long-time friend and fellow Gulag specialist (author of the excellent, Gulag Town, Company Town), whose work and support over the years have meant a tremendous amount to me, and who has definitely made my own work stronger.
On that last note, I’m also very pleased to be part of a roundtable discussion at the CAS titled, “New Directions in Gulag Studies,” chaired by Lynne Viola (my mentor and dissertation advisor), and also including comments from Alan Barenberg, Steve Maddox, and Sean Kinnear. It should be a great conference!
 Moreover, in almost all of those murders there was an intimate connection between the victim and the perpetrator (they were close relatives, or lovers, or married, and so on). Dr. Kesselring thus questioned if the method of murder in the Igantii case (strangulation) meant that the relationship between Ignatii and the pupils was somehow closer than might appear (perhaps there had been some abuse, for example?).
Moreover, in almost all of those murders there was an intimate connection between the victim and the perpetrator (they were close relatives, or lovers, or married, and so on). Dr. Kesselring thus questioned if the method of murder in the Igantii case (strangulation) meant that the relationship between Ignatii and the pupils was somehow closer than might appear (perhaps there had been some abuse, for example?).


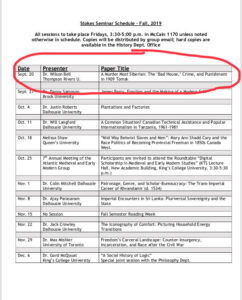 at Dalhousie. I took German and Holocaust history courses with him, and was especially fond of the tangential stories he would tell related to certain historical figures and events.
at Dalhousie. I took German and Holocaust history courses with him, and was especially fond of the tangential stories he would tell related to certain historical figures and events.


